Suggestions for Follow-up Actions (KS3-MS2-1: Students can use the formulas for circumferences and areas of circles) (11 Feb 2014, accessible on tablet devices)
Possible problems in students' learning (for reference only)
- Students do not recognize that the value circumference ÷ diameter is a constant.
- Students do not know that π = circumference ÷ diameter.
- Students think that 22/7 and 3.14 are the exact values of π..
- Students mix up the formulas for circumferences and areas of circles.
- Students mix up the diameter with radius when they use the formulas.
Suggestions for Follow-up Actions
| Name | Emphasis | Description | Problem addressed (see above) | Suggested duration (minutes) | Available for self - learning? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Circumference and Diameter
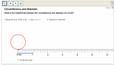 |
Recognize the relationship between circumferences and diameters | With the HTML5 dynamic figure and the worksheet, students measure the circumferences of circles of diameters 1 cm, 2 cm, 3 cm and other diameters. By calculating the value of π = circumference ÷ diameter, students recognize that the circumference is about 3.14 times the diameter and the formula for the circumference. | 
|
25 |  |
Area of Circles
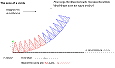 |
Explore the formula for the area of circles | With the HTML5 dynamic figure and the worksheet, students dissect a circle into sectors. By rearranging the sectors and increasing the number of sectors, students explore the formula for the area of the circle by observing the shape obtained when the number of sectors tends to infinity. | 
|
25 |  |
Other Resources
- OR, C.M. (to be published). Pedagogical Design Focusing on Learning Difficulties – Area of Circles. Assessment and Learning, 1.
http://wlts.edb.hkedcity.net/filemanager/file/mathematics/tc/ks3/ks3ms21/other_resource/or(2012)_circle_area.pdf
Comming Soon

